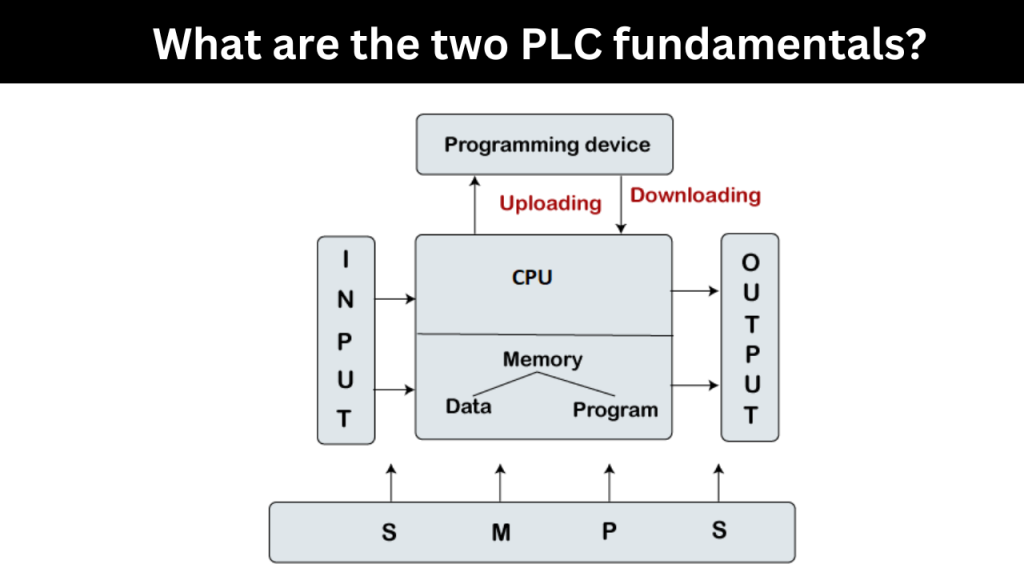
PLCs, or programmable logic controllers, are digital computer devices that are used in industrial automation to control and observe machinery or processes. Two PLC basics exist:
-
Inputs:
Numerous sensors, switches, and other devices are utilised to monitor the condition of the system or process being controlled, and these inputs are used to code PLCs. These inputs provide information on the current events or situations, such as temperature, pressure, location, level, or switch status. Examples of additional sorts of input devices include limit switches, proximity sensors, temperature sensors, pressure transmitters, and others. The PLC continually scans these inputs to detect changes and update its internal state.
- Limit switches: To identify whether an object is there or not, these mechanical switches make direct physical touch with it. They are widely employed to locate moving components, such as doors, and to monitor door movement.
- Proximity sensors: These sensors use a range of technologies (inductive, capacitive, and optical) to detect the presence or absence of an item without making physical touch. Proximity sensors are frequently used for level detection, position sensing, or item identification in industrial applications.
- Temperature sensors: These sensors generate analogue or digital signals that, after determining the temperature of a system or environment, represent the temperature value. Examples of typical kinds are thermistors, resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), and thermocouples.
- Pressure transmitters: These devices measure the pressure of the liquid or gas and convert it into an electrical signal that the PLC can comprehend. Pressure transmitters are often used to measure and control pressure levels in industrial operations.
- Flow meters: Flow metres are used to measure fluid flow rates, including those of gases and liquids. They provide information on the volume, flow rate, or total volume of fluid passing through a pipe or conduit.
- Level sensors: In tanks, silos, or other storage facilities, these sensors measure the volume of liquid or solid items present. By keeping an eye on and controlling the filling or emptying process, they aid in maintaining goal levels.
- Switches and buttons: To initiate certain operations or control modes, straightforward pushbuttons or switches are utilised as manual inputs. They can be used for operator interfaces or emergency stop processes.
Check: Allen Bradley MicroLogix 1400 PLC
-
Outputs:
PLCs may also control a variety of output devices, including as motors, valves, solenoids, pumps, and indicators. The PLC’s outputs are used to carry out operations based on the input signals and the control logic that has been programmed into it. When it determines that a set of requirements have been satisfied, the PLC activates the corresponding output devices, compelling them to switch on, off, or modify their settings. This enables the PLC to automate and regulate the functioning of machinery and procedures.
- Motors: PLCs control electric motors, which are used to power machinery or other equipment. Depending on the kind of motor and the application, PLCs may start, stop, and control the speed and direction of motors. Motors are used extensively in conveyor systems, robotic arms, pumps, fans, and many other industrial applications.
- Valves: PLCs have the ability to open, close, or adjust valves in order to regulate the flow of liquids, gases, or other substances through a system. In the industrial, water treatment, and oil and gas industries, valves are widely used to control the flow and distribution of fluids.
- Solenoids: Switches, levers, and valves may all be controlled mechanically by solenoids, which are electromagnetic devices. PLCs have the ability to turn solenoids on or off to control the position or movement of mechanical parts in a system.
- Pumps: In systems like water supply, chemical dosing, or circulation systems, PLCs may start, stop, or modify the flow rate of pumps.
- Start/Stop Control: A pump can be started or stopped by PLCs depending on the situation. To monitor the level in a tank, for instance, the PLC may employ level sensors. When the level falls below a set threshold, the Rockwell Automation 1766-L32BXBA MicroLogix 1400 PLC may start the pump to indicate that more fluid is needed. On the other hand, when the level reaches a specific level, the PLC can instruct the pump to shut off.
- Speed Control: In some circumstances, a pump’s speed may need to be adjusted in order to accurately control the flow rate. PLCs may regulate pumps equipped with variable frequency drives (VFDs) or other speed control devices. The flow rate is controlled by the pump motor’s speed, which is altered by the PLC by altering the output frequency or voltage of the VFD.
- Indicators and displays: Indicators like as lights, LEDs, or digital displays can be controlled by PLCs to show operators important information or to offer visual feedback about the state of the system.
- Alarms and sirens: PLCs have the ability to activate sirens, warning devices, or audible or visual alarms to alert operators to potentially hazardous conditions or system defects.
- Communication interfaces: PLCs commonly provide output features for communicating with other systems or devices. This includes the transmission of signals to additional PLCs, computers, Human-Machine Interface (HMI) panels, or other control systems.
Finally, inputs provide the PLC with information about the state of the system, while outputs enable the PLC to act and regulate the system based on the logic that has been programmed and the input circumstances. Because they handle inputs and generate outputs, PLCs are the brains of industrial automation systems.
Automation Parts Supplier Asteam Techno Solutions Pvt Ltd is well known in this sector. You may get industrial automation components from us; our products are of the highest quality, and our customer service is unmatched. We offer new and used components online, and we have a sizable selection of products from the most well-known manufacturers, like Allen Bradley, Schneider, Siemens, Moxa, Vipa, and more. We support providing them with high-quality goods from dependable vendors and utilising our broad expertise to assist them.