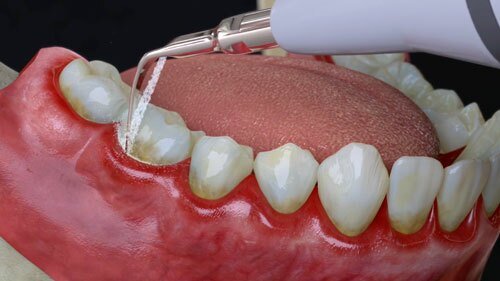
Gingivitis, a common oral health issue, affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by inflamed and bleeding gums, gingivitis is often a precursor to more severe dental problems, including bone loss. Fortunately, effective gingivitis treatment and bone graft dental procedures can help individuals regain their oral health and prevent further complications. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes and symptoms of gingivitis, discuss the importance of bone grafting, and delve into the various treatment options available.
Gingivitis is an early stage of gum disease that occurs when plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, accumulates on the teeth and gums. This buildup leads to irritation and inflammation of the gum tissue, resulting in the following common symptoms:
Prompt treatment of gingivitis is crucial to prevent it from progressing into more severe forms of gum disease, such as periodontitis, which can lead to bone loss and tooth mobility. Here are some effective gingivitis treatment options:
In cases where gingivitis has progressed to periodontitis and bone loss has occurred, bone graft dental procedures become necessary. Bone grafting is a surgical technique that involves the transplantation of bone tissue to repair damaged or missing bone. This procedure is essential for restoring the structural integrity of the jawbone and providing support for teeth.
Gingivitis treatment and bone graft dental procedures are vital aspects of maintaining oral health and preventing more severe dental issues. Early detection and prompt treatment of gingivitis can often prevent the need for extensive dental procedures like bone grafting. However, if bone loss has occurred, bone grafts provide an effective solution for restoring the jawbone’s structure and supporting dental implants. Remember that regular dental check-ups and consistent oral hygiene practices are the best ways to prevent gingivitis and the associated complications. If you suspect you may have gingivitis or require a bone graft, consult with a qualified dentist to discuss your treatment options.